Dental implants are a long-term tooth replacement option. Learn how assessment, bone support, and aftercare are approached in oral and maxillofacial care.
Introduction
Dental implants are commonly used to replace missing teeth and restore oral function. While implants are widely discussed, successful treatment depends on careful assessment, appropriate planning, and ongoing care.
This article explains how dental implants are evaluated within oral and maxillofacial practice, what factors influence suitability, and why long-term maintenance is essential.
What Is a Dental Implant?
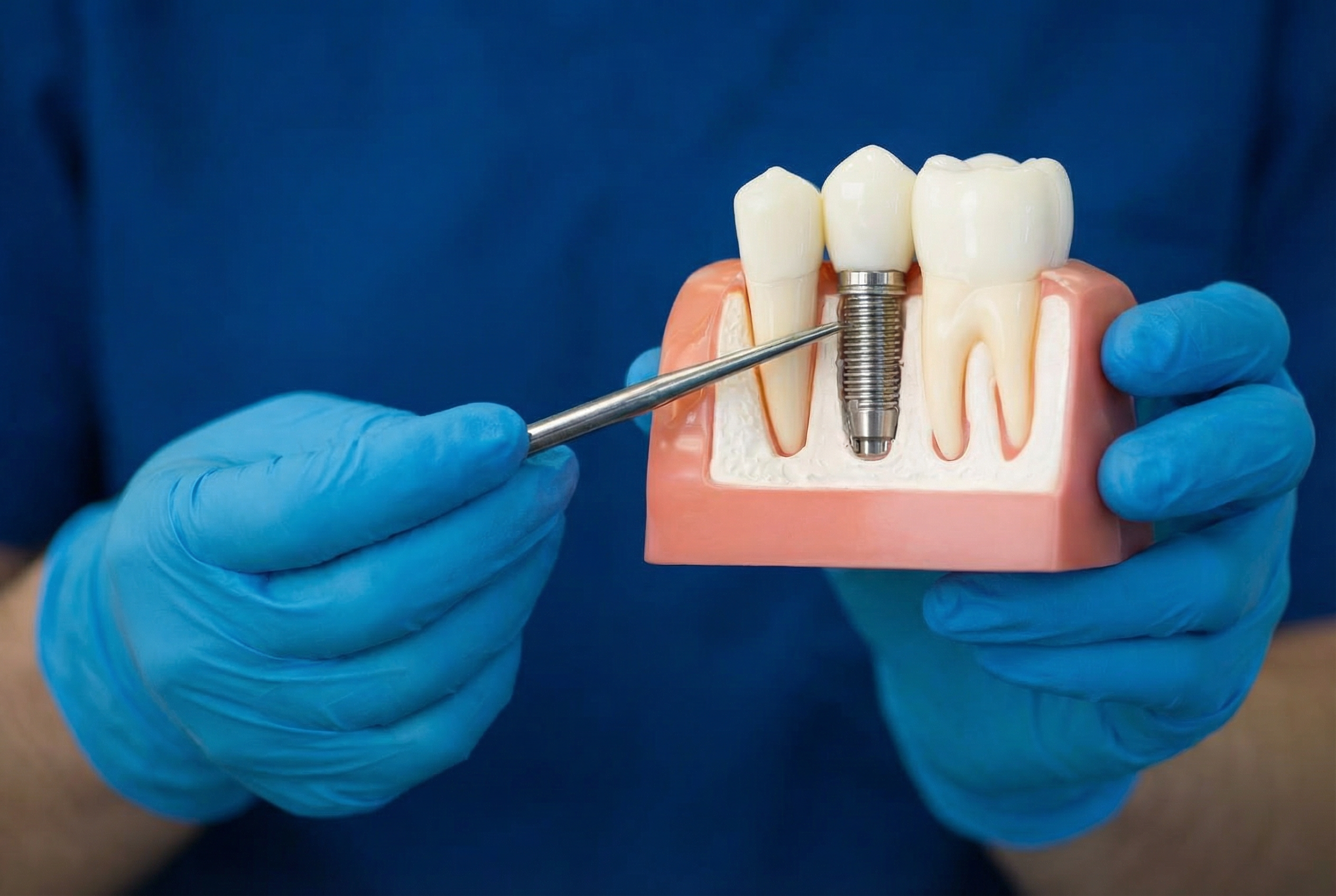
A dental implant is a small, medical-grade titanium fixture placed into the jawbone to support a crown, bridge, or denture. Over time, the surrounding bone integrates with the implant surface, helping provide stability.
According to **:contentReference[oaicite:3]{index=3}**, dental implants are one of several tooth replacement options and are considered when oral health and bone conditions are suitable.
https://www.healthhub.sg/a-z/treatments/dental-implant
Dental implants differ from removable options because they rely on bone support rather than resting on the gums.
Who May Be Suitable for Dental Implants?
Dental implants are not suitable for everyone. An oral and maxillofacial assessment considers factors such as:
– Gum and bone health
– Location of the missing tooth
– Medical history and medications
– Oral hygiene practices
Suitability is determined on an individual basis rather than age alone.
For broader context, patients may also wish to read **[tooth replacement options explained]**.
Why Bone Support Matters
Bone support plays an important role in implant stability. After tooth loss, bone volume may reduce gradually over time. In the upper jaw, the maxillary sinus can also limit available bone height.
Assessment focuses on:
– Bone quantity and density
– Position of adjacent structures
– Healing capacity
Academic institutions such as the **:contentReference[oaicite:4]{index=4}** emphasise structured evaluation before implant placement.
https://www.nuhs.edu.sg/nucohs
Bone Grafting and Sinus Lift Procedures
When bone volume is insufficient, preparatory procedures may be discussed. These can include:
– Bone grafting to support implant placement
– Sinus lift procedures in the upper jaw
These procedures are not required for all patients and are recommended only when assessment findings suggest they may support implant planning.
You may find **[sinus lift and bone grafting explained]** helpful for understanding these procedures.
The Dental Implant Treatment Process
Implant treatment typically involves several stages:
1. **Assessment and planning**
2. **Implant placement**
3. **Healing period** for bone integration
4. **Final restoration** of the tooth
Timelines vary depending on individual healing and treatment complexity. These stages are discussed in detail during consultation.
Aftercare and Long-Term Maintenance
Dental implants require ongoing care similar to natural teeth. Long-term considerations include:
– Daily oral hygiene
– Regular professional reviews
– Monitoring of surrounding gum and bone health
The **:contentReference[oaicite:5]{index=5}** notes that maintenance and follow-up are important for long-term implant health.
https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/dental-implant/about/pac-20384622
Patients may also find **[dental implant aftercare and maintenance]** useful.
Setting Realistic Expectations
While dental implants are well-established, outcomes vary. Healing response, general health, and adherence to aftercare advice all influence long-term results.
Clear discussion of benefits, limitations, and alternatives supports informed decision-making and realistic expectations.
Conclusion
Dental implants are a reliable option for replacing missing teeth when planned carefully and maintained appropriately. Through structured assessment, imaging-supported planning, and patient education, oral and maxillofacial care supports safe and informed implant treatment.
Patients considering implants may also wish to explore **[what to expect during an oral and maxillofacial consultation]**.
References & Further Reading
HealthHub Singapore – Dental Implants
https://www.healthhub.sg/a-z/treatments/dental-implant
National University Centre for Oral Health Singapore
https://www.nuhs.edu.sg/nucohs
Mayo Clinic – Dental Implants
https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/dental-implant/about/pac-20384622